When you order pressed blanks or rolled and sliced blanks (RS), please provide a drawing for the polished lens. After you provide the drawing for the polished lens, we will prepare the press drawing taking into account the production methods and technical requirements for pressed blanks as well as applying the following standards.
1. Diameter and Thickness
1.1 DP and RP Blanks
The allowance and tolerance (range) of the diameter and thickness (center thickness) for DP blanks and RP blanks are as shown in Tables 4 and 5. Since the availability of DP blanks are limited by the glass type and the shape, please contact us for further information.
Table 4 DP: Allowance and Tolerance (Range) of Diameter and Thickness (unit: mm)
| Diameter(φ) | Diameter | Thickness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allowance | Tolerance (Range) | Allowance | Tolerance (Range) |
|
| 18 ≦ φ < 30 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| 30 ≦ φ < 50 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| 50 ≦ φ < 70 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| 70 ≦ φ < 100 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| 100 ≦ φ < 120 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
Table 5 RP: Allowance and Tolerance (Range) of Diameter and Thickness (unit: mm)
| Diameter(φ) | Diameter | Thickness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allowance | Tolerance (Range) | Allowance | Tolerance (Range) |
|
| < 18 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| 18 ≤ φ < 30 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| 30 ≤ φ < 50 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| 50 ≤ φ < 70 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| 70 ≤ φ < 100 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| 100 ≤ φ < 120 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| 120 ≤ φ < 180 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 1.0 |
| ≧ 180 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
1.2 Rolled and Sliced Blanks (RS)
The allowance and tolerance (range) of the diameter and thickness (center thickness) for RS blanks are as shown in Table 6.
Table 6 RS: Allowance and Tolerance (Range) of Diameter and Thickness (unit: mm)
| Diameter(φ) | Tolerance of Diameter (Range) | Tolerance of Thickness (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 ≤ φ ≤ 20 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
2. Radius Curvature (R)
2.1 Guideline for Curvature Value
The reference value of R of pressed blanks is set so that their glass outer portion, which is thicker than that of polished blanks, contacts the machine before the inner portion during processing. That is, the R of pressed blanks is larger (gentler) than that of polished blanks in the case of convex R, while the R of pressed blanks is the smaller (sharper) in the case of concave R. To indicate the thickened value for the outer potion, the difference from the height of the spherical segment (Δh) is used. It is set as shown in Table 7. In the case of convex R, Δh is reduced from the height of the spherical segment of the polished blanks. In the case of concave R, Δh is added to the height of the spherical segment of the polished blanks.
Table 7 Thickened Value for Outer Portion (Δh) (unit: mm)
| Diameter(φ) | Thickened Value for Outer Portion(Δh) |
|---|---|
| φ < 70 | 0.3 |
| 70 ≤ φ < 100 | 0.4 |
| 100 ≤ φ < 180 | 0.6 |
| 180 ≤ φ | 1.0 |
[Example of conversion from the Polished Blank dimension to the Pressed Blank dimension]
For example, when the dimension of a DP blank is converted from a polished blank dimension to a pressed blank dimension based on the standards outlined above, the results are as shown in Table 8. Also, the results are as shown in Fig. 1. (Chamfering is omitted.)
Table 8 Example of Conversion from Polished Blank Dimension to Pressed Blank Dimension
(DP Blank) (unit: mm)
| Dia. | Thickness | Concave R | Convex R | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | R1 | h | R2 | |||
| Polished Lens |
50.0 | 3.0 | 4.81* | 70.0 | 3.31* | 100.0 |
| Pressed Blanks |
51.0 | 4.0 | 4.81+0.3 | 66.2 | 3.31-0.3 | 109.5 |
* The value of the outer diameter of the Pressed Blank.
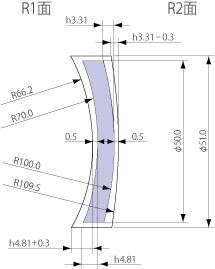
Fig. 1
Example of Conversion from the Polished
Blank Dimension to the Pressed Blank
Dimension
2.2 Accuracy of the Radius Curvature
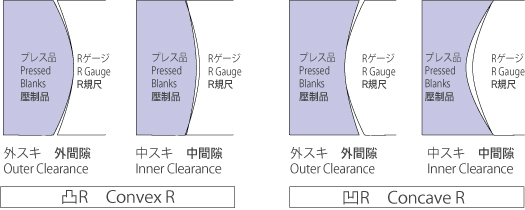
The accuracy of the radius curvature of actually produced pressed blanks is evaluated using the clearance (outer clearance and inner clearance) between the R of pressed blanks and the reference R gauge as shown in Fig. 2. The allowance is as shown in Table 9.
Table 9 Allowance of the Accuracy of R (unit: mm)
| Dia.(φ) | Allowance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | |||
| Outer Clearance | Inner Clearance | Outer Clearance | Inner Clearance | |
| φ < 70 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| 70 ≤ φ < 120 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
Note: In cases in which application of this standard is difficult due to the shape and the glass type, or in the case of diameters ≥120, we will consult with customers separately.
Fig. 2 Evaluation Method for the Accuracy of R
2.3 R1 side in HOYA's drawings
For the R side of Pressed Blanks, the directions suited to our press properties and customers processing properties are employed rather than the standard illustration method for optical designs.
The R1 side of pressed blanks on our press drawings is indicated in accordance with Table 10. This side is the upper side of the press die.
Table 10 Description of R1 Side
| Shape of Pressed Blanks | R1 Side |
|---|---|
| Bi-Convex | Shallow Side (side with the gentle R) |
| Plano-Convex | Flat Side (∞ side) |
| Bi-Concave | Deep Side (side with the sharp R) |
| Plano-Concave | Concave Side |
| Meniscus | Convex Side |
3. Inside Diameter
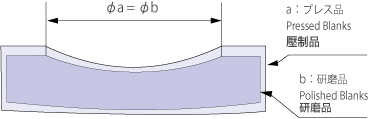
In the case of a shape with an inside diameter, the inside diameter of pressed blanks (φa) will have the same dimension as that of polished blanks (φb), as shown in Fig 3.
Fig.3 Dimension of Inside Diameter of Pressed Blanks
4. Chamfering
To avoid cracking or chipping of pressed blanks, chamfering is added to the outer periphery of pressed blanks if the following conditions are met.(Fig.4)
In general, the Chamfering is indicated by C plane chamfering. (Plane crossing processed 45°)
The size of added chamfering is as shown in Table 11.
Fig.4 Chamfering and Edge Thickness
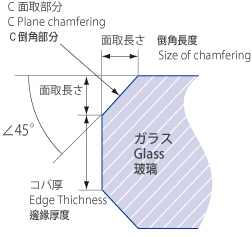
Table 11 Size of Chamfering
| Diameter (φ) | Size of Chamfering |
|---|---|
| φ < 15 | 0.3 |
| 15 ≤ φ < 100 | 0.5 |
| 100 ≤ φ < 180 | 1.0 |
| 180 ≤ φ | 2.0 |





